The how-to guides linked on this page illustrate how to integrate Azure Synapse Analytics with Immuta. See the reference guide for information about the Azure Synapse Analytics integration.
Requirement: A running Dedicated SQL pool
These guides provide instructions on getting your data set up in Immuta.
Configure your Azure Synapse Analytics integration: Configure an Azure Synapse Analytics integration with Immuta so that Immuta can create policy protected views for your users to query.
Register Azure Synapse Analytics data sources: This will register your data objects into Immuta and allow you to start dictating access through global policies.
Organize your data sources into domains and assign domain permissions to accountable teams: Use domains to segment your data and assign responsibilities to the appropriate team members. These domains will then be used in policies.
These guides provide instructions on getting your users set up in Immuta.
Connect an IAM: Bring the IAM your organization already uses and allow Immuta to register your users for you.
Map external user IDs from Azure Synapse Analytics to Immuta: Ensure the user IDs in Immuta, Azure Synapse Analytics, and your IAM are aligned so that the right policies impact the right users.
These guides provide instructions on getting your data metadata set up in Immuta.
Connect an external catalog: Bring the external catalog your organization already uses and allow Immuta to continually sync your tags with your data sources for you.
Run identification: Identification allows you to automate data tagging using identifiers that detect certain column names.
These guides provide instructions on using the Governance app for the first time.
Author a global subscription policy: Once you add your data metadata to Immuta, you can immediately create policies that utilize your tags and apply to your tables. Subscription policies can be created to dictate access to data sources.
Author a global data policy: Data metadata can also be used to create data policies that apply to data sources as they are registered in Immuta. Data policies dictate what data a user can see once they are granted access to a data source. Using catalog tags you can create proactive policies, knowing that they will apply to data sources as they are added to Immuta with the automated tagging.
Configure audit: Once you have your data sources and users, and policies granting them access, you can set up audit export. This will export the audit logs from policy changes and tagging updates.
In this integration, Immuta generates policy-enforced views in a schema in your configured Azure Synapse Analytics Dedicated SQL pool for tables registered as Immuta data sources.
This guide outlines how to integrate Azure Synapse Analytics with Immuta.
Azure Synapse Analytics configuration: Configure the integration in Immuta.
Azure Synapse Analytics integration reference guide: This guide describes the design and components of the integration.
Azure Synapse Analytics pre-configuration details: This guide describes the prerequisites, supported features, and limitations of the integration.
This page provides a tutorial for enabling the Azure Synapse Analytics integration on the Immuta app settings page. To configure this integration via the Immuta API, see the Integrations API getting started guide.
For an overview of the integration, see the Azure Synapse Analytics overview documentation.
A running Dedicated SQL pool is required.
Click the App Settings icon in the left sidebar.
Click the Integrations tab.
Click the +Add Integration button and select Azure Synapse Analytics from the dropdown menu.
Complete the Host, Port, Immuta Database, and Immuta Schema fields.
Opt to check the Enable Impersonation box and customize the Impersonation Role name as needed. This will allow users to natively impersonate another user.
Opt to update the User Profile Delimiters. This will be necessary if any of the provided symbols are used in user profile information.
You have two options for configuring your Azure Synapse Analytic environment:
Automatic setup: Grant Immuta one-time use of credentials to automatically configure your environment and the integration.
Manual setup: Run the Immuta script in your Azure Synapse Analytics environment yourself to configure the integration.
Enter the username and password in the Privileged User Credentials section.
Select Manual.
Download, fill out the appropriate fields, and run the bootstrap master script and bootstrap script linked in the Setup section.
Enter the in the Immuta System Account Credentials section. The username and password provided must be the credentials that were set in the bootstrap master script when you created the user.
Click Save.
Register Azure Synapse Analytics data in Immuta.
Click the App Settings icon in the left sidebar.
Navigate to the Integrations tab and click the down arrow next to the Azure Synapse Analytics Integration.
Edit the field you want to change. Note any field shadowed is not editable, and the integration must be disabled and re-installed to change it.
Enter Username and Password.
Click Save.
Click the App Settings icon in the left sidebar.
Navigate to the Integrations tab and click the down arrow next to the Azure Synapse Analytics Integration.
Click the checkbox to disable the integration.
Enter the username and password that were used to initially configure the integration.
Click Save.
This page describes the Azure Synapse integration, configuration options, and features. See the Azure Synapse integration page for a tutorial on enabling the integration and these features through the app settings page.
❌
❌
✅
❌
✅
A running Dedicated SQL pool
Immuta only supports the SQL authentication option for Azure Synapse Analytics to configure the integration and create data sources. The Microsoft Entra authentication option is unsupported. See the SQL Authentication in Azure Synapse Analytics documentation for details.
Immuta cannot ingest tags from Synapse, but you can connect any of these supported external catalogs to work with your integration.
Impersonation allows users to query data as another Immuta user in Synapse. To enable user impersonation, see the User Impersonation page.
A user can configure multiple integrations of Synapse to a single Immuta tenant.
Immuta does not support the following masking types in this integration because of limitations with Dedicated SQL pools (linked below). Any column assigned one of these masking types will be masked to NULL:
Reversible Masking: Synapse UDFs currently only support SQL, but Immuta needs to execute code (such as JavaScript or Python) to support this masking feature. See the Synapse Documentation for details.
Format Preserving Masking: Synapse UDFs currently only support SQL, but Immuta needs to execute code (such as JavaScript or Python) to support this masking feature. See the Synapse Documentation for details.
Regex: The built in string replace function does not support full regex. See the Synapse Documentation for details.
The delimiters configured when enabling the integration cannot be changed once they are set. To change the delimiters, the integration has to be disabled and re-enabled.
If the generated view name is more than 128 characters, then the view name is shortened to 128 characters. This could cause collisions between view names if the shortened version is the same for two different data sources.
For proper updates, the Dedicated SQL pools have to be running when changes are made to users or data sources in Immuta.
This page describes the Azure Synapse Analytics integration, through which Immuta applies policies directly in Azure Synapse Analytics. For a tutorial on configuring Azure Synapse Analytics see the Azure Synapse Integration page.
The Azure Synapse Analytics is a policy push integration that allows Immuta to apply policies directly in Azure Synapse Analytics Dedicated SQL pools without the need for users to go through a proxy. Instead, users can work within their existing Synapse Studio and have per-user policies dynamically applied at query time.
This integration works on a per-Dedicated-SQL-pool basis: all of Immuta's policy definitions and user entitlements data need to be in the same pool as the target data sources because Dedicated SQL pools do not support cross-database joins. Immuta creates schemas inside the configured Dedicated SQL pool that contain policy-enforced views that users query.
When the integration is configured, the Application Admin specifies the
Immuta database: This is the pre-existing database Immuta uses. Immuta will create views from the tables contained in this database, and all schemas and views created by Immuta will exist in this database, such as the schemas immuta_system, immuta_functions, and the immuta_procedures that contain the tables, views, UDFs, and stored procedures that support the integration.
Immuta schema: The schema that Immuta manages. All views generated by Immuta for tables registered as data sources will be created in this schema.
User profile delimiters: Since Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pools do not support array or hash objects, certain user access information is stored as delimited strings; the Application Admin can modify those delimiters to ensure they do not conflict with possible characters in strings.
For a tutorial on configuring the integration see the Azure Synapse Integration page.
Synapse data sources are represented as views and are under one schema instead of a database, so their view names are a combination of their schema and table name, separated by an underscore.
For example, with a configuration that uses IMMUTA as the schema in the database dedicated_pool, the view name for the data source dedicated_pool.tpc.case would be dedicated_pool.IMMUTA.tpc_case.
You can see the view information on the data source details page under Connection Information.
This integration uses webhooks to keep views up-to-date with the corresponding Immuta data sources. When a data source or policy is created, updated, or disabled, a webhook is called that creates, modifies, or deletes the dynamic view in the Immuta schema. Note that only standard views are available because Azure Synapse Analytics Dedicated SQL pools do not support secure views.
The status of the integration is visible on the integrations tab of the Immuta application settings page. If errors occur in the integration, a banner will appear in the Immuta UI with guidance for remediating the error.
The definitions for each status and the state of configured data platform integrations is available in the response schema of the integrations API. However, the UI consolidates these error statuses and provides detail in the error messages.
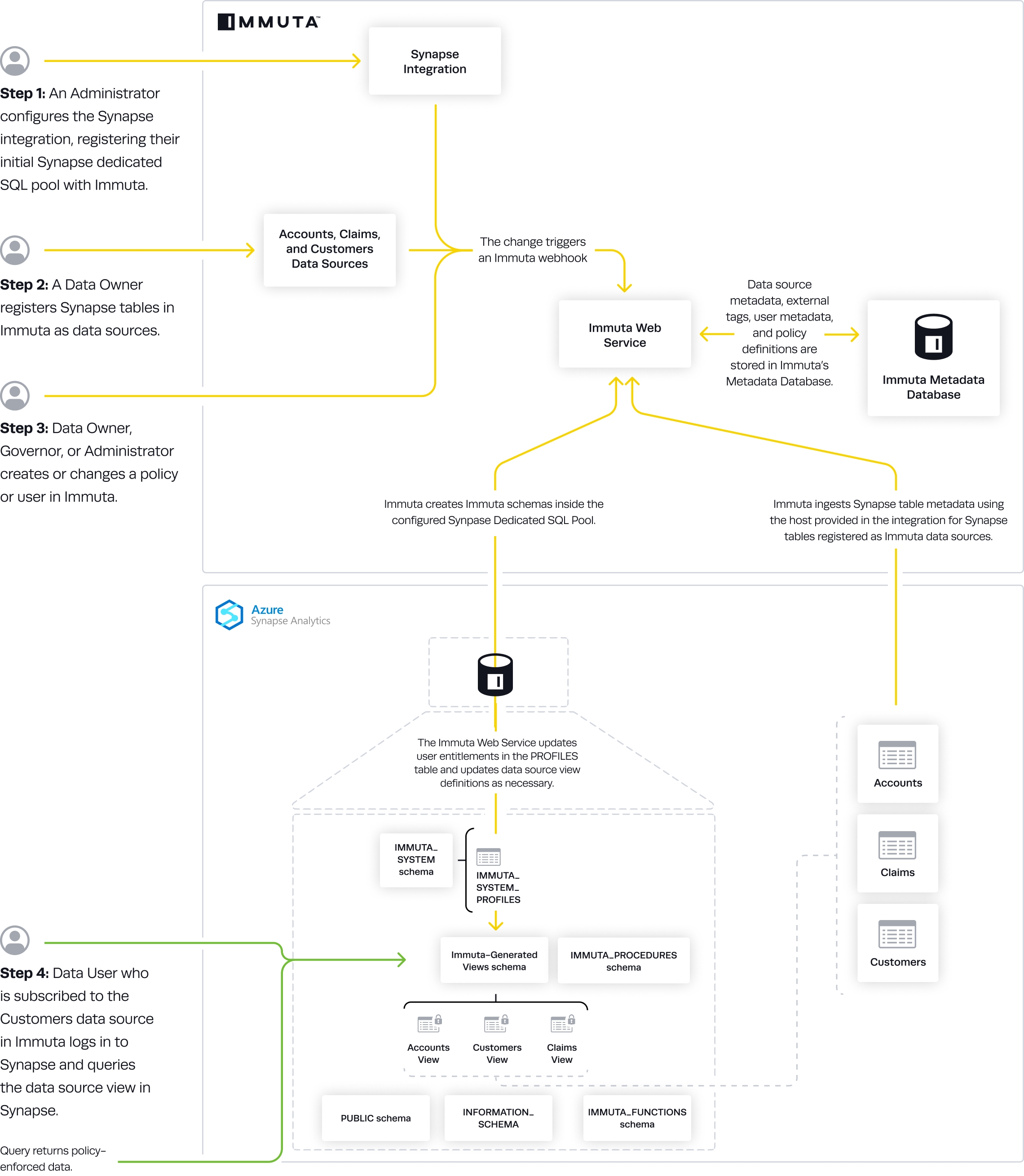
An Immuta Application Administrator configures the Azure Synapse Analytics integration, registering their initial Synapse Dedicated SQL pool with Immuta.
Immuta creates Immuta schemas inside the configured Synapse Dedicated SQL pool.
A Data Owner registers Azure Synapse Analytics tables in Immuta as data sources. A Data Owner, Data Governor, or Administrator creates or changes a policy or user in Immuta.
Data source metadata, tags, user metadata, and policy definitions are stored in Immuta's Metadata Database.
The Immuta Web Service calls a stored procedure that modifies the user entitlements or policies and updates data source view definitions as necessary.
An Azure Synapse Analytics user who is subscribed to the data source in Immuta queries the corresponding data source view in Azure Synapse Analytics and sees policy-enforced data.
