Custom REST Catalog Interface Endpoints
The custom REST catalog integration allows Immuta to make a defined set of API calls to a custom REST service you develop to retrieve metadata. The custom REST service receives Immuta's calls, and then collects the relevant information and delivers it back to Immuta, allowing you to build and maintain your own solutions that provide metadata required to effectively use Immuta within your organization.
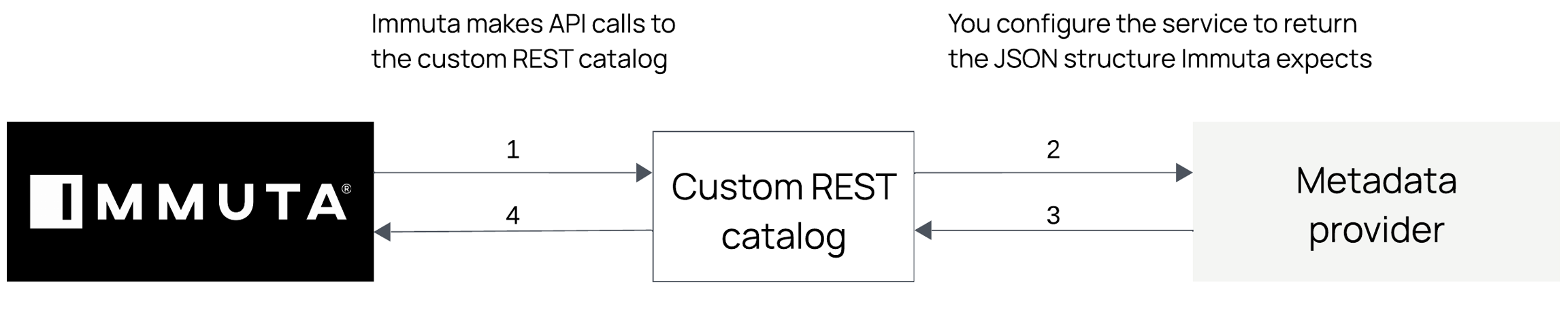
The custom-developed service must be built to receive and handle calls to the REST endpoints specified below. Immuta will call these endpoints when certain events occur and at various intervals. The required responses to complete the connection are detailed below.
General concepts
Tags
Tags are attributes applied to data at the data-source-level or at the column-level.
Tags in Immuta take the form of a nested tree structure:
The REST catalog interface interprets a tag's relationship mapping from a string based on a standard dot (.) notation:
Tags returned must meet the following constraints:
They must be no longer than 500 characters. Longer tags will not throw an error but will be truncated silently at 500 characters.
They must be composed of letters, digits, underscores, dashes, and whitespace characters. A dot (
.) is used as a delimiter as described above. Other special characters are not supported.
A tag object has a single id property, which is used to uniquely identify the tag within the catalog. This id may be either a string or integer type, and its value is up to the designer of the REST catalog service. Common examples include a standard integer value, a UUID, or a hash of the tag's string value (if it is unique within the system).
For this example REST catalog interface, tags are represented in a JSON object. The object below specifies 3 different tags:
For more information on tags and how they are created, managed, and displayed within Immuta, see the Tag reference guide.
Descriptions
Descriptions are strings that can be applied to either a data source or an individual column. These strings support UTF-8, including special and various language characters.
Authentication
Immuta can make requests to your REST catalog service using any of the following authentication methods:
Username and password: Immuta can send requests with a username and a password in the authorization HTTP header. In this case, the custom REST service will need to be able to parse a basic authorization header and validate the credentials sent with it.
PKI certificate: Immuta can also send requests using a CA certificate, a certificate, and a key.
No authentication: Immuta can make unauthenticated requests to your REST catalog service. However, this should only be used if you have other security measures in place (e.g., if the service is in an isolated network that's reachable only by your Immuta environment).
Authentication and specific endpoints
When accessing the /dataSource and /tags endpoints, Immuta will use the configured username and password. If you choose to also protect the human-readable pages with authentication, users will be prompted to authenticate when they first visit those pages.
Endpoints
GET /tags
/tagsThe /tags endpoint is used to collect ALL the tags the catalog can provide. It is used by Immuta to populate Immuta's tags list on the tags page. These tags can then be used for policy creation ahead of actual data sources being created that make use of them. This enables policies to immediately apply when data sources are registered with Immuta.
As with all external catalogs, tags ingested by Immuta from the REST catalog interface cannot be modified locally within Immuta, since this catalog is the source of truth for them.
Request
Response
The custom REST service must respond with an object that maps all tag name strings to associated ids. The tag name string fully-qualifies the location of the tag in the tree structure, and the id is a globally unique identifier assigned by the REST catalog to that tag.
POST /dataSource
/dataSourceThe /dataSource endpoint does the majority of the work. It receives a POST request from Immuta, and returns the mapping of a data source and its columns to the applied tags and descriptions.
Immuta will try to fetch metadata for a data source in the system at various times:
During data source creation. During data source creation, Immuta will send metadata to the REST catalog service, most notably the connection details of the data source, which includes the schema and table name. It is important that the custom REST service implemented can parse this information and search its records for an appropriate record to return with an ID unique to this data source in its
catalogMetadataobject.When a user manually links the data source. Data sources that either fail to auto-link or that were created prior to the custom REST catalog being configured can still be manually linked. To do so, a data source owner can provide the ID of the asset as defined by the custom REST catalog via the Immuta UI. In order for this to work, the custom REST catalog service must support matching data source assets by unique ID.
During various refreshes. Once linked, Immuta will periodically call the
/dataSourceendpoint to ensure information is up to date.
Request
Immuta's POST requests to the /dataSource endpoint will consist of a payload containing many of the elements outlined below.
catalogMetadata
dictionary
Object holding the data source's catalog metadata.
catalogMetadata.id
string or integer
The unique identifier of the data source in the catalog.
catalogMetadata.name
string
The name of the data source in the catalog.
handlerInfo
dictionary
Object holding the data source's connection details.
handlerInfo.schema
string
The data source’s schema name in the source system.
handlerInfo.table
string
The data source’s table name in the source system.
handlerInfo.hostname
string
The data source’s connection schema in the source storage system.
handlerInfo.port
integer
The data source’s connection port in the source storage system.
handlerInfo.query
string
The data source’s connection schema in the source storage system, if applicable.
dataSource
dictionary
Object holding general data source information from Immuta. This can be viewed with debugging, but is not usually required for catalog purposes.
This object must be parsed by the custom REST catalog in order to determine the specific data source metadata being requested.
Immuta will provide the id of the data source as part of the catalogMetadata. This should be used as the primary metadata lookup value.
When a data source is being created, such an id will not yet be known to Immuta. Immuta will instead send handlerInfo information as part of the request.
When an id is not specified, the schema and table name elements should be parsed in an attempt to identify the desired catalog entry and provide an appropriate id. If such a lookup is successful and an id is returned to Immuta in the catalogMetadata section, Immuta will establish an automatic link between the new data source and the catalog entry, and future references will use that id.
Response
The schema for the /dataSource response uses the same tag object structure from the /tags response, along with the following set of metadata keys for both data sources and columns.
catalogMetadata
dictionary
Object holding the data source's catalog metadata.
catalogMetadata.id
string or integer
The unique identifier of the data source in the catalog.
catalogMetadata.name
string
The name of the data source in the catalog.
description
string
A description of the data source.
tags
<tags object>
Object containing the data source-level tags.
dictionary
dictionary
Object containing the column names of the data source as its keys.
dictionary.<column>
dictionary
Object containing a single column's metadata.
dictionary.<column>.catalogMetadata.id
string or integer
The unique identifier of the column in the catalog.
dictionary.<column>.description
string
A description of the column.
dictionary.<column>.tags
<tags object>
Object containing the column-level tags as keys.
Example
GET /dataSource/page/{id}
/dataSource/page/{id}This endpoint returns a human-readable information page from the REST catalog for the data source associated with {id}. Immuta provides this as a mechanism for allowing the REST catalog to provide additional information about the data source that may not be directly ingested by or visible within Immuta. This link is accessed in the Immuta UI when a user clicks the catalog logo associated with the data source.
Request
Immuta will send a GET request to the /dataSource/page/{id} endpoint.
id
URL parameter, integer, or string
The unique identifier of the data source in the remote catalog system.
Example
Response
The custom REST catalog can either provide such a page directly, or can redirect the user to any resource where the appropriate page would be provided - for example a backing full service catalog such as Collibra, if this custom REST catalog is simply being used to support a custom data model.
GET /column/{id}
/column/{id}This endpoint returns the catalog's human-readable information page for the column associated with {id}. Immuta provides this as a mechanism for allowing the REST catalog to provide additional information about the specific column that may not be directly ingested by or visible within Immuta.
Request
Immuta will send a GET request to the /column/{id} endpoint.
id
URL parameter, integer, or string
The unique identifier of the column in the remote catalog system.
Example
Response
The custom REST catalog can either provide such a page directly, or it can redirect the user to any resource where the appropriate page would be provided. For example, it could redirect to a backing full service catalog such as Collibra, if the custom REST catalog is simply being used to support a custom data model.
Last updated
Was this helpful?

