Domains Reference Guide
Domains are containers of data sources that allow you to assign data ownership and access management to specific business units, subject matter experts, or teams at the nexus of cross-functional groups. Within a domain, specific users are assigned a domain permission to manage policies, audit, and run identification on the data sources in that domain, which eliminates the problem of centralizing your data governance and giving users too much power over all data in your organization. Instead, you can control how much power these users have over data by restricting their privileges to the domains you specify.
Once a data owner registers data as Immuta data sources, users with the GOVERNANCE permission can add data sources to domains based on business units, business goals, or policy management strategy within their organization. Then, a user with the USER_ADMIN permission can assign additional users to audit activity on data sources or manage policies on data within those domains:
Domain data sources
Data sources can be assigned to domains based on business units in your organization or any other method that suits your business goals and policy management strategy. Users with the GOVERNANCE permission choose to assign data sources to a domain one of two ways:
Manually: Every data source in the domain is selected by the
GOVERNANCEuser and added to or removed from the domain through actions in the UI or API.Dynamically: Data sources are assigned to the domain based on data source table tags selected by the
GOVERNANCEuser; column tags cannot be used for dynamic domain assignment. Data sources are automatically added to or removed from the domain continuously without user intervention based on whether they have the selected tag. Any tag in Immuta can be used for domain assignment (e.g., an external catalog tag or a tag manually applied by a user). See how data source are assigned dynamically below.
Once a data source is assigned to a domain (or multiple domains), users with a domain permission can start performing actions on those data sources.
See the Getting started with domains guide for instructions on creating a domain and adding data sources to it.
Performance
Adding data sources to a domain, whether dynamically with auto-assign or manually using bulk actions, will take longer the more data sources you are adding. The following scenarios are regularly tested in order to provide a benchmark of the average time to complete the action.
Scenario 1
Add 1,000 data sources to a domain.
<1 second on average
Scenario 2
Add 10,000 data sources to a domain.
2 seconds on average
Scenario 3
Add 100,000 data sources to a domain.
30 seconds on average
Domain policies
Whether created within or outside a domain, Immuta policies enforce access as usual: users who meet the restrictions outlined in the policy applied to a data source may access that data source. However, domains restrict who can author policies that apply to data sources assigned to that domain. This policy management restriction gives organizations more control of how much power governance users have over data. Furthermore, it can make Immuta easier to use by allowing more people to author policies.
Users with the Manage Policies permission in a domain can set global policies to apply to the domains for which they have the Manage Policies permission. In the example below, the domain policy manager can only apply global policies to the HR domain:
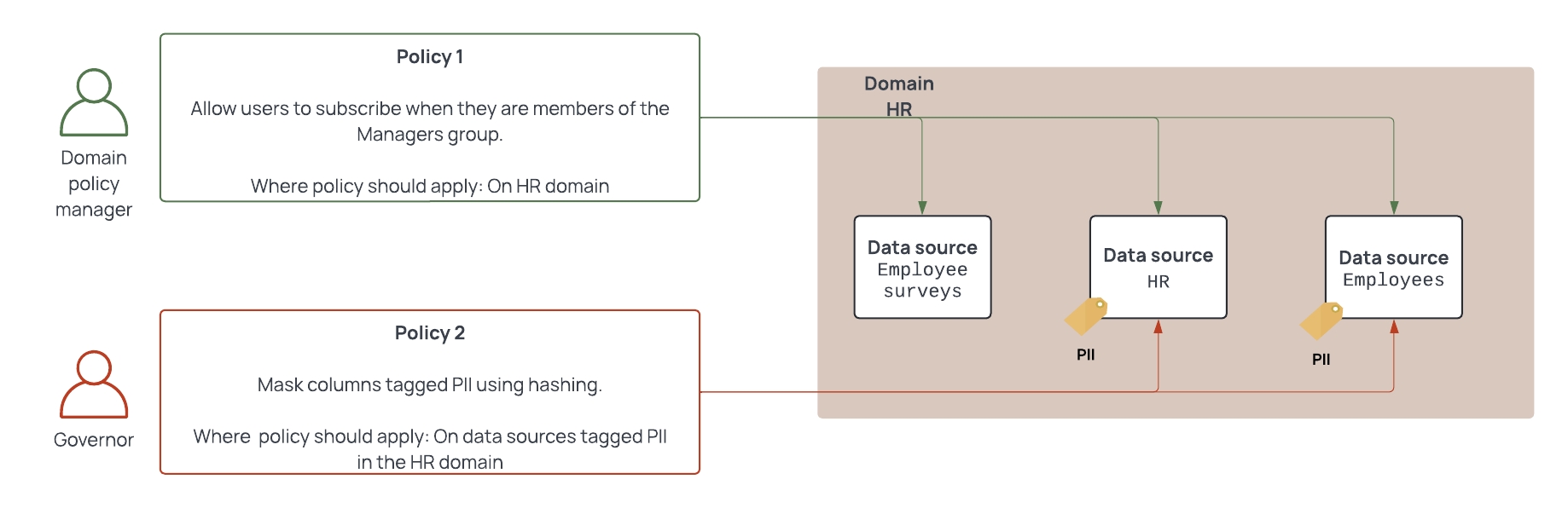
If that same user had the Manage Policies permission for the HR and Marketing domains, they could write global policies to apply to data sources within both of those domains. If that user had the Manage Policies permission on all domains in their organization or the global GOVERNANCE permission, they could set global policies to apply to all data sources.
When a data source is removed from or added to a domain, Immuta recomputes the policies that apply to the domain. Any policies associated with a domain will be added to or removed from a data source when it is added to or removed from the domain.
See the Getting started with domains guide for instructions on authoring domain policies.
Designing domain policies
When integrating domains to distribute policy management across your organization, data governance and access control must be applied horizontally (globally across data in your organization) and vertically (locally within specific domains or data products). Global policies should be authored and applied in line with your ecosystem’s most generic and all-encompassing principles, regardless of the data’s domain. For example, a global policy could be used to mask all PII data across an organization. Domain or local policies, on the other hand, should be fine-grained and applicable to only context-specific purposes or use cases. For example, a domain or local policy could be used to only show rows in the Sales table where the value in the country column matches the user's office location.
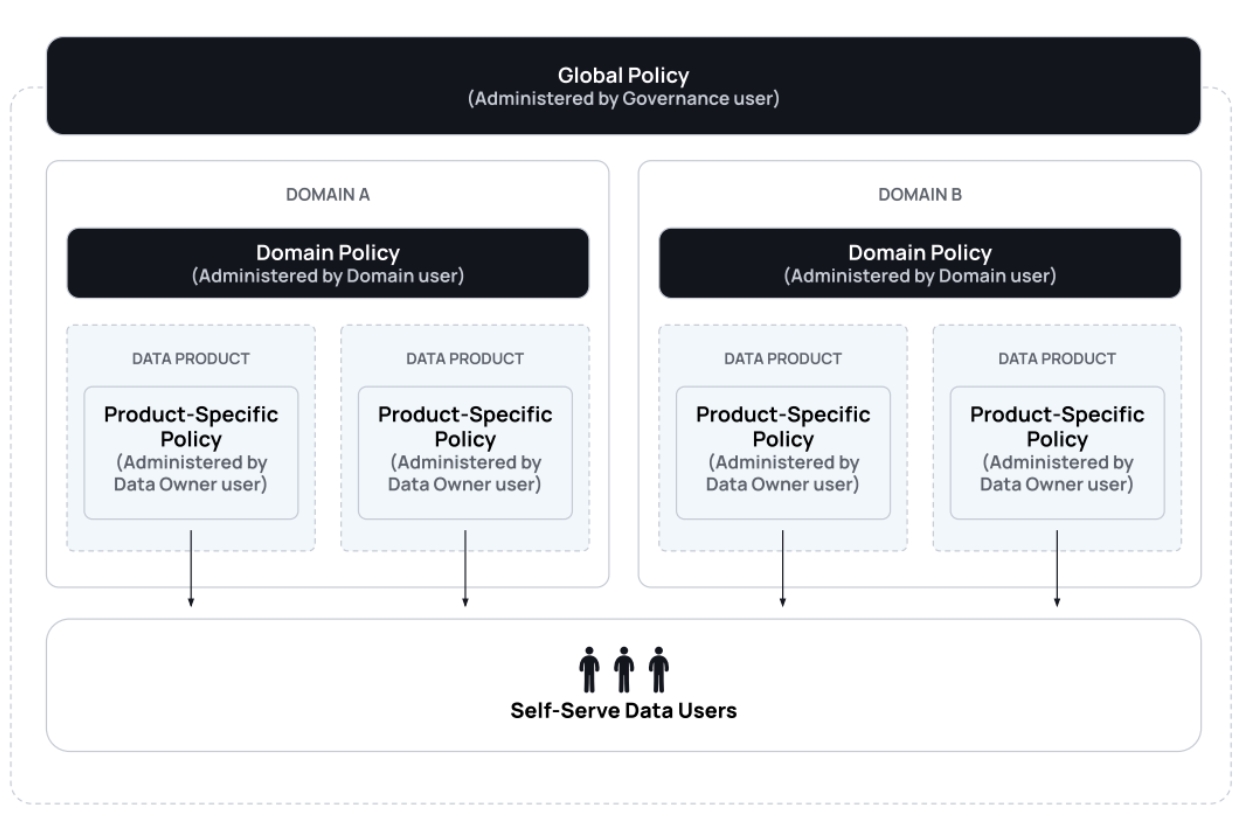
These three different policy levels are authored by separate users:
Global policy level: Users with the
GOVERNANCEpermission can create global policies that apply to all data sources in an organization.Domain policy level: Users with the
Manage Policiespermission can apply policies to data sources within the domains for which they have that permission.Local policy level: Data owners can apply policies directly to a data source, even if a domain or global policy applies to it as well. Because they are the most knowledgeable of their data, data owners can disable and apply the most relevant policy to their data source.
Since policies apply to domain data sources at multiple levels, there are instances in which two or three policies could apply to a single domain data source. Data owners can disable and enable policies that are most appropriate for their data source when a conflict occurs. For details about policy conflicts, merges, and policy conflict management, see the following pages:
Audit
Users with the global AUDIT permission can see all audit events throughout Immuta. To scope this audit information to just a single domain, users can be given the domain Audit Activity permission.
Domain events
The following domain-related events are audited and can be found on the audit page in the UI:
DomainCreated: A domain is created.
DomainDataSourcesUpdated: Data sources are assigned to or removed from a domain.
DomainDeleted: A domain is deleted.
DomainPermissionsUpdated: A domain-specific permission is applied to or removed from a user or group.
DomainUpdated: A domain's details (name, description, settings etc.) are updated.
Data source assignment
The following events related to data source assignment are audited and can be found on the audit page in the UI:
DomainDataSourcesUpdated: Data sources are assigned to or removed from the domain.
TagApplied: A tag is applied to a data source or column, which could lead to a data source being added to a domain.
TagRemoved: A tag is removed from a data source or column, which could lead to a data source being removed from a domain.
Activity tab
If a user has the domain Audit Activity permission on a particular domain, they can see domain-specific audit events in the Activity tab of the domain. The following domain activities are in that tab:
Domain: Events from when the domain was created, permissions were updated, and the domain was updated.
Data sources: Events from the data sources within the specific domain.
Policies: Events for policies created, edited, or deleted that affect data sources within the domain.
Queries: Events for user queries against data sources within the domain.
Deleting a domain
Users with the GOVERNANCE permission can delete any domain that has zero data sources assigned to it.
See the Getting started with domains guide for instructions on deleting a domain.
Migrating to domains
Existing data sources can be assigned to a domain by a user with the GOVERNANCE permission. Once added to a domain, domain policies will be enforced on the data sources.
See the Getting started with domains guide for instructions on adding existing data sources to a domain.
Permissions
Domain permissions can be added to users or groups by a user with the USER_ADMIN Immuta permission. See the Permissions and personas page for a list of global and domain permissions necessary to manage domains.
Last updated
Was this helpful?

